In the motor manufacturing industry, the efficiency and precision of rotor automatic loading and unloading assembly lines are directly related to product quality and the company’s competitiveness. Vacuz will delve into the core standards of rotor automatic loading and unloading assembly lines and key strategies for optimizing production methods. We will also demonstrate the effectiveness of these standards and strategies in actual production, using practical application cases. We hope this will be helpful!
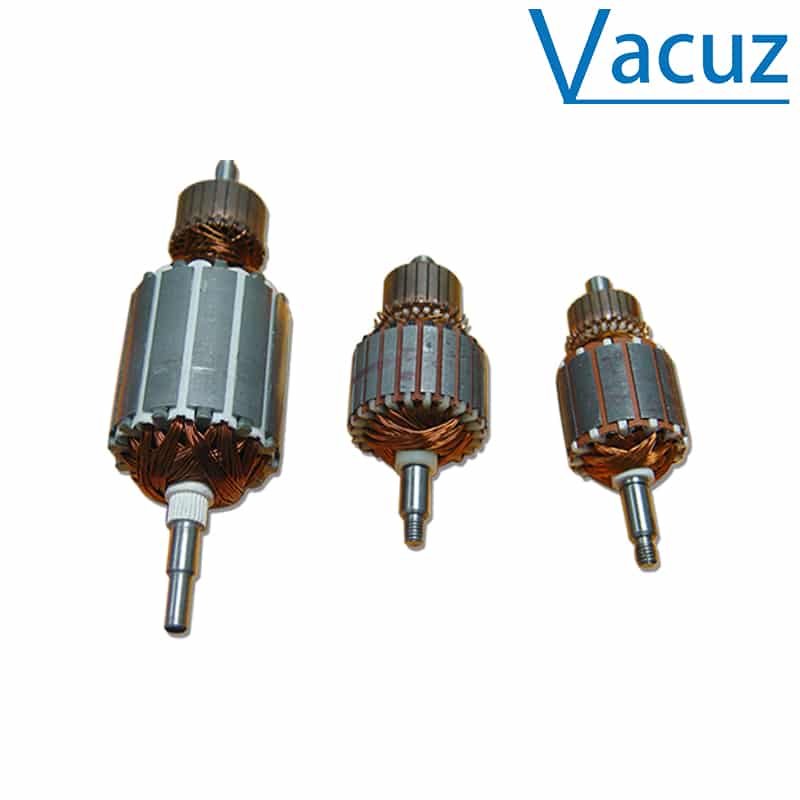

Alta velocidad automática cepillado armadura rotor estator motor bobina ranura cuña aislante papel inserción montaje máquina
I. Core Standards for Rotor Automatic Loading and Unloading Assembly Lines
1. Equipment Accuracy and Stability Standards
a. Hardware Configuration: To ensure the accuracy and stability of the production line, a high-rigidity machine frame, precision ball screws, and a high-resolution servo drive system are required. For example, the flying fork rotating mechanism must undergo rigorous dynamic balancing tests, with vibration amplitude controlled within 0.05mm to prevent deflection caused by centrifugal force during high-speed operation.
b. Drive System: Low-friction, highly wear-resistant linear guides or direct drive (DD) systems are selected to eliminate mechanical transmission backlash and reduce motion lag. One company successfully improved positioning repeatability from ±0.1mm to ±0.02mm by replacing traditional belt drives with linear motors.
c. Environmental Adaptability: The equipment must operate stably in an environment with a temperature of 20-25°C and a humidity of 40-60% RH. It must be equipped with air springs or magnetorheological dampers to effectively suppress external vibration interference.
2. Automation and Intelligent Standards
a. Loading and unloading system: The system integrates a vibrating plate, conveyor belt, and robotic arm to enable automated feeding and sorting of parts. A vision guidance system (such as a 3D camera) identifies the rotor core’s orientation, achieving a positioning accuracy of ±0.02mm and ensuring alignment error between the magnetic slots and the core within 0.05mm.
b. Process Parameter Control: Step-by-step speed control is implemented via a PLC or industrial PC, and linked to a tension control system to accommodate varying wire diameters and stator slot configurations. This helps ensure production process stability and product quality.
c. Data Traceability and Feedback: RFID tags or QR code scanning systems are installed to record process parameters, operators, and test results for each batch of products in real time. This enables quality traceability back to the raw material batch, helping to improve product quality and customer satisfaction.
3. Quality Inspection and Safety Standards
a. In-Process Inspection: Integrated inductance testers, insulation resistance testers, and dynamic balancing testers enable 100% process inspection. This helps ensure product compliance with relevant standards and customer requirements.
b. Safety Protection: Equipment must comply with IEC 60204-1 electrical safety standards and be equipped with leakage protection, overload protection, and an emergency stop button. Light barriers or safety gates should be installed in the operating area to prevent personnel from accidentally entering the danger zone.
c. Material Management: Utilize high-bay warehouses and automated guided vehicle (AGV) systems to enable automated material distribution and inventory monitoring. This helps reduce the risk of injury from manual handling and improves production efficiency.
II. Key Strategies for Optimizing Production Methods
1. Parallelization and Modular Design
a. Process Splitting: Serial processes are split into parallel workstations, seamlessly connected via AGVs or high-speed conveyors. This helps improve equipment utilization and production efficiency.
b. Modular Layout: Utilize a U-shaped production line layout to shorten material handling distances and support rapid changeovers. Parametric programming enables flexible production of different rotor models to meet diverse market demands.
2. Integration of High-Speed Equipment and Complex Processes
a. High-Speed Winding Machines: Select winding machines with speeds ≥5000 rpm, combined with torque control technology, to ensure winding accuracy. This helps improve production speed and product quality.
b. Multi-Station Complex Equipment: Integrates winding, wire inserting, and press-fitting functions, reducing workpiece turnover. This helps shorten production cycle times and equipment footprint.
3. Intelligent Inspection and Predictive Maintenance
a. AI Defect Detection: Leveraging deep learning algorithms to build an intelligent inspection system, this system automatically identifies defects such as broken enameled wire and misaligned inserts. This improves inspection accuracy and production efficiency.
b. Predictive Maintenance: Vibration sensors are installed on key components, providing early warning of failures through big data analysis. This helps reduce equipment downtime and maintenance costs.
4. Lean Management and Continuous Improvement
a. PDCA Cycle: Establish a “Plan-Do-Check-Act” mechanism, hold regular quality improvement meetings, analyze production line operating data, and develop optimization measures. This helps continuously improve production line efficiency and quality.
b. Personnel Training and Incentives: Regularly conduct operational skills training and establish incentive mechanisms to stimulate employee innovation. This helps improve employee skills and production enthusiasm.
Alta velocidad automática cepillado armadura rotor estator motor bobina ranura cuña aislante papel inserción montaje máquina
In summary, optimizing rotor automatic loading and unloading assembly lines requires addressing multiple aspects: equipment accuracy and stability, automation and intelligence, quality inspection and safety, parallelization and modular design, integration of high-speed equipment and complex processes, intelligent inspection and predictive maintenance, and lean management and continuous improvement. By implementing these standards and strategies, companies can significantly improve production efficiency and product quality, enhancing their market competitiveness.
Correo electrónico: sales@vacuz.com





