Evaluating brushless stator internal and external winding machines requires comprehensive consideration of five dimensions: applicable scenarios, equipment configuration, winding details, debugging requirements, and production efficiency. There are significant differences between the two in winding methods, speeds, applicable wire diameters, and equipment complexity. Below, Vacuz provides a simple analysis!
I. Comparison of Evaluation Dimensions
1. Applicable Scenarios and Product Types
Internal Winding Machine: Suitable for stators with inward-facing slots (such as power tools, water pumps, household appliances, medical devices, etc.). Winding is completed by the up-and-down movement of a needle bar in conjunction with a mold.
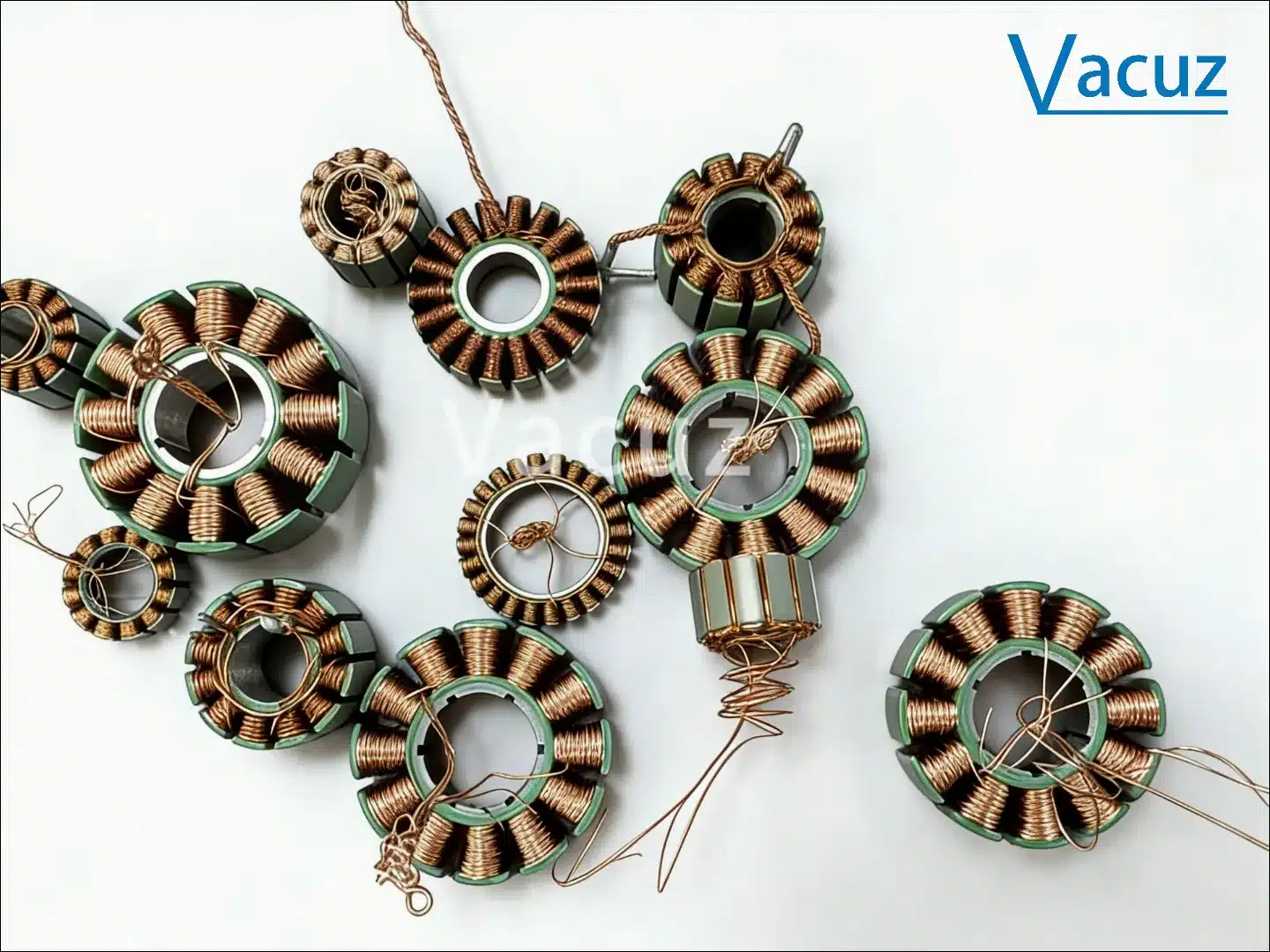
External Winding Machine: Suitable for stators with outward-facing slots (such as model airplanes, drones, fascia guns, balance scooters, etc.). It uses a high-speed rotating fork winding method, with the wire entering the slot from the outside.
2. Equipment Configuration and Complexity
Internal Winding Machine: Typically equipped with a high-precision servo motor and motion controller. It requires a professional mold and wire arrangement system, and has high requirements for equipment stability.
External winding machine: Relatively simple configuration; ordinary equipment can use stepper motors or servo motors, but the configuration complexity may exceed that of an internal winding machine for precision wiring requirements.
3. Differences in winding details
Winding method:
Internal winding machines use needle winding. Winding is completed by the up-and-down and back-and-forth movement of the needle bar and wire nozzle, combined with the left-and-right movement of the die. Suitable for multi-wire winding (e.g., two-wire, three-wire, four-wire), but it is prone to damage or breakage when the wire diameter exceeds 0.5mm.
External winding machines use a fly fork winding system. A high-speed rotating fly fork winds the wire into the slot, supporting multi-wire winding (e.g., 30 wires can be wound together for diameters below 0.3mm). However, it is necessary to ensure that the slot spacing is wide enough to avoid wire overlap or scratching.
Speed and efficiency:
Internal winding machines are generally slower, reaching speeds of up to 1000 RPM, limited by the screw or belt drive structure.
External winding machines are faster, with ordinary equipment reaching 3000 RPM, and high-end equipment even reaching 5000 RPM. Wire Diameter Adaptability:
Internal winding machines are suitable for fine wires (e.g., around 0.1mm). The thicker the wire, the more difficult the winding becomes, requiring a tension control system.
External winding machines are more adaptable to different wire diameters, but when winding thicker wires, the slot distance and wire feeding angle need optimization.
4. Debugging and Optimization Requirements
Internal Winding Machine:
Focus on optimizing the synchronization of the needle bar’s up-and-down movement and the die’s left-and-right movement to avoid uneven wire feeding or damage.
High die precision is required (e.g., polishing degree Ra≤0.4μm, clearance between the locating pin and stator hole≤0.01mm).
External Winding Machine:
The rotation angle of the fly fork and the stability of the wire nozzle movement need optimization to reduce the number of wire bends.
The fly fork diameter is typically 80%-90% of the stator’s outer diameter to ensure uniform wire coverage of the slots.
5. Production Efficiency and Yield
Internal Winding Machine: Single slot winding time approximately 8-12 seconds, wire damage rate ≤0.2%, wire breakage rate ≤0.1%.
External Winding Machine: Single slot winding time approximately 5-8 seconds, higher efficiency, but requires strict control of slot distance and wire arrangement accuracy to avoid wire overlap.
II. Selection Recommendations
Based on stator slot direction: Choose an internal winding machine if slots face inwards, and an external winding machine if slots face outwards.
Based on wire diameter and parallel winding requirements: Prioritize external winding machines for fine wires or multi-wire parallel winding; choose internal winding machines for thick wires or high accuracy requirements.
Based on production efficiency requirements: Choose external winding machines for high-speed production; choose internal winding machines for high winding accuracy and stability.
Based on budget and equipment maintenance costs: Internal winding machines have higher configuration and cost, but are suitable for long-term high-accuracy production; external winding machines offer flexible configuration and relatively lower cost.

How to evaluate brushless stator internal and external winding machines? What are the differences in winding details? The above provides a simple explanation of Vacuz, and I hope this information will be helpful!

