Different motor stator winding machines and different customer needs require different winding standards. To improve winding effect and quality, the wound products must be inspected. So, what are the winding standards for fully automatic motor stator winding machines? How to check if the winding is qualified? Vacuz will give you a brief introduction below!
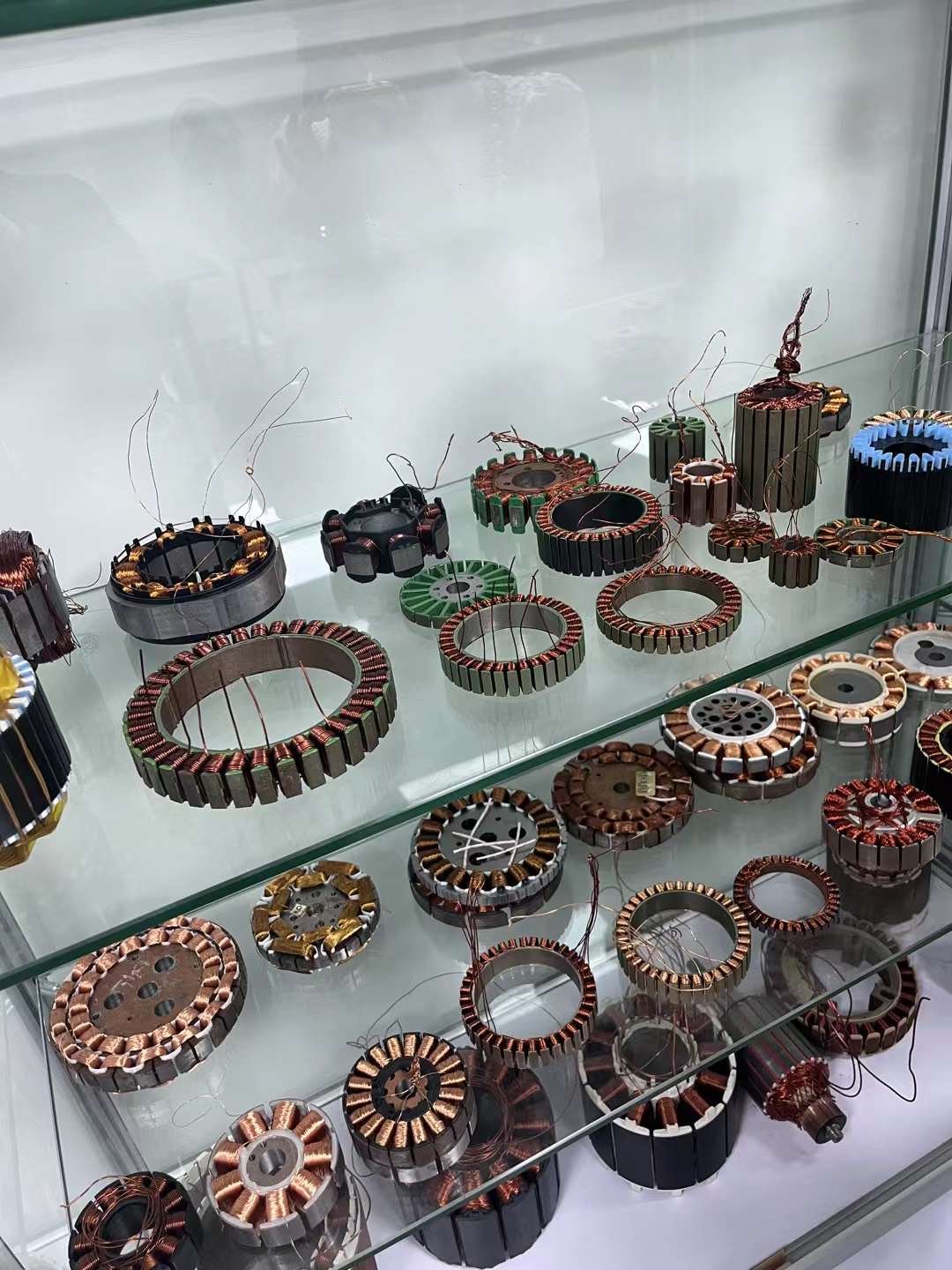

I. Core Standards for Winding
1. Winding Method and Precision
Free-form winding: Relies on wire tension and the oscillation of the swing wheel to achieve coil layout. It is necessary to ensure accurate spacing between the guide wheel and the frame, and that each turn of wire is tightly and evenly wound.
Forced winding: Through precise synchronization technology between the main shaft and the winding shaft, the winding mechanism advances a preset distance (usually the wire diameter) for each turn, and the error must be controlled within ±0.01mm.
Path planning: Based on the stator slot shape, a three-dimensional mathematical model is established to generate a smooth winding path, reducing wire bending stress and adapting to dynamic adjustments for different slot shapes (such as trapezoidal and rectangular).
2. Tension Control
Intelligent Tension Adjustment System: Automatically adjusts tension based on wire material (copper/aluminum), wire diameter, and winding speed. Copper wire tension range: 0.5-5N; Aluminum wire: 0.3-3N; fluctuation must be ≤±0.5N.
Closed-Loop Feedback System: Monitors tension in real time and optimizes the curve to prevent wire breakage or loosening, ensuring tension uniformity.
3. Spindle and Wire Laying Speed Matching
The spindle speed and wire laying speed must be accurately synchronized. During high-speed winding (e.g., spindle speed > 5000 RPM), a closed-loop servo system and vibration suppression algorithm are required to control the jitter amplitude within ±0.01mm.
4. Die and Equipment Precision
The die must be made of high-strength material with a positioning error ≤±0.05mm to prevent loosening or shaking during winding.
The wire nozzle is made of ceramic or tungsten carbide and equipped with a pneumatic/electric micro-adjustment mechanism to compensate for minute changes in wire diameter in real time.
5. Winding Parameter Settings
Based on stator parameters (outer diameter, inner diameter, height, number of slots, wire diameter, etc.), preset the program number, number of coil turns, winding speed, and other parameters to ensure they match production requirements.
II. Winding Qualification Inspection Methods
1. Visual Inspection
Coil flatness and compactness: Coils should be neatly arranged, without overlapping, crossing, or looseness, and the slot fill factor should be uniform.
Enameled wire insulation layer: Check the insulation layer for integrity, without damage, scratches, or softening.
End height and insulation distance: End extension lengths must be consistent, end heights must meet drawing requirements, and an insulation distance must be maintained from the frame, shaft, and other parts.
2. Electrical Performance Testing
Insulation resistance test: Use a megohmmeter to measure the insulation resistance of each phase winding to ensure it meets the standard (usually ≥100MΩ).
DC resistance test: Measure the resistance of each phase winding using a precision resistance tester; the allowable difference is ≤±2%.
Withstand Voltage Test: Apply a specified high voltage (e.g., 2 times rated voltage + 1000V) for 1 minute without breakdown.
Three-Phase Current Balance Test: Apply a low voltage (3-10% of rated voltage), the difference between the maximum and minimum three-phase currents should be ≤ ±3% of the average value.
3. Wiring Accuracy Inspection
Laser Displacement Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of copper wire position, deviation ≤ ±0.05mm.
Visual Inspection System: Scans the winding surface to identify defects such as missing wires and overlaps, with a defect detection accuracy ≥ 99.5%.
Slot Filling Rate: The copper wire filling rate must meet design requirements, avoiding excessive density (heat dissipation issues) or excessive sparseness (performance degradation).
4. Functionality and Safety Tests
Salt Water Test: After winding, immerse in salt water and check if the leakage current meets the standard (usually ≤ 0.5mA).
No-Load Operation Test: Run the equipment for 30 minutes and check if the bearings and moving parts overheat (temperature ≤ 60℃) or produce abnormal noise (≤ 65dB).
Pinhole Test: Detects for leakage points in the windings, ensuring no wire damage.
III. Key Control Points
Environmental Control: Operates in a workshop with a temperature of 20±2℃ and humidity of 50±5% to prevent softening of the enameled wire insulation.
Process Database: Establishes a database containing stator models, wire specifications, and winding parameters, supporting rapid parameter matching.
Operator Training: Regularly trains operators on equipment operation, parameter adjustment, and troubleshooting skills, ensuring wire spacing tolerance ≤ ±0.03mm.
What are the winding standards for fully automatic motor stator winding machines? How to check if the winding is qualified? Vacuz has provided a simple explanation above; we hope this information is helpful!
