Fully automatic stator winding machines perform winding and wire arrangement simultaneously. Different types of winding machines have different winding and wire arrangement methods. The accuracy of parameters is also crucial during winding and wire arrangement. So, what are the winding and wire arrangement methods for fully automatic stator winding machines? How can parameter accuracy be ensured? Vacuz will give you a brief introduction below!
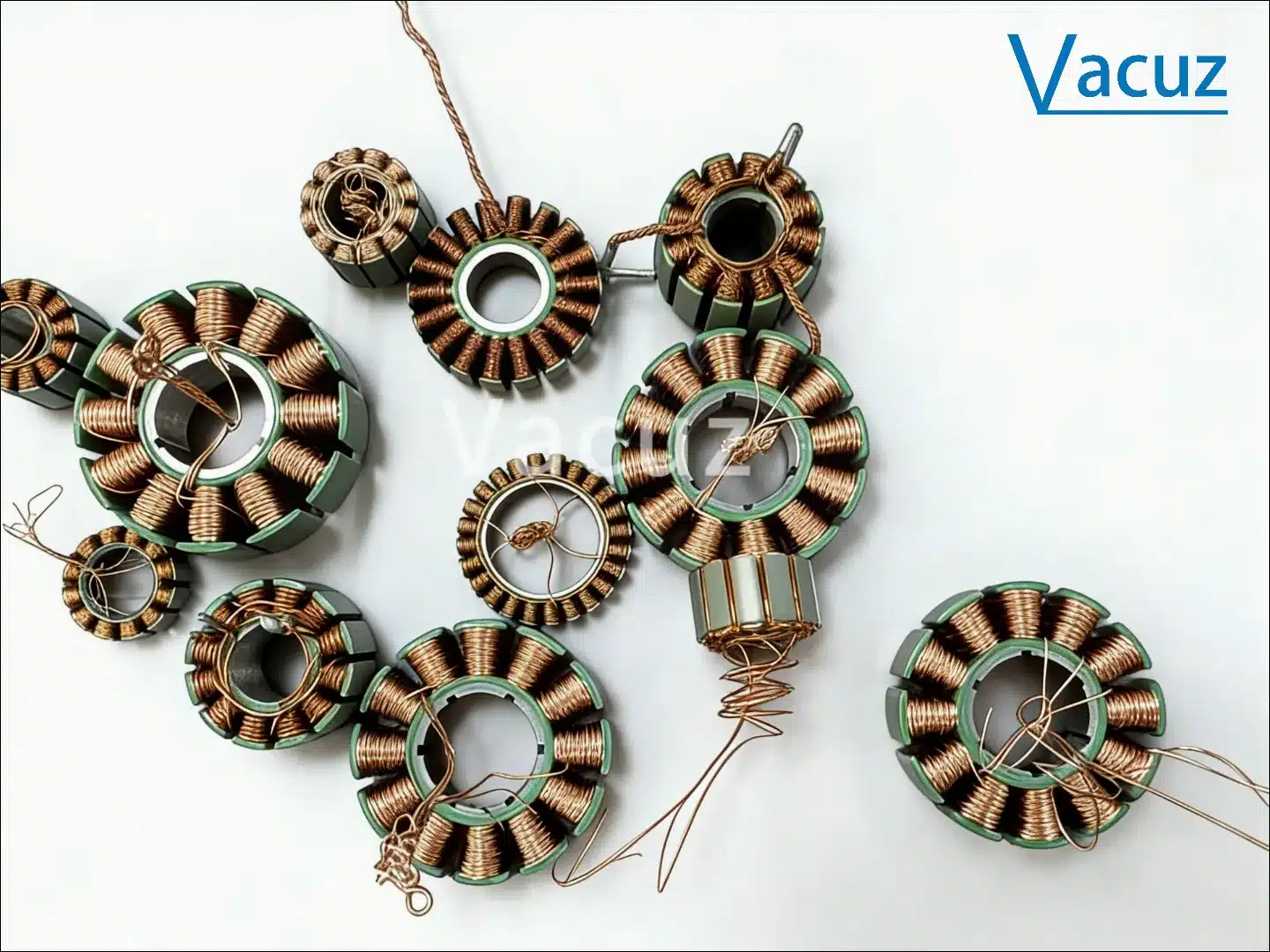

I. Winding and Wire Arrangement Methods
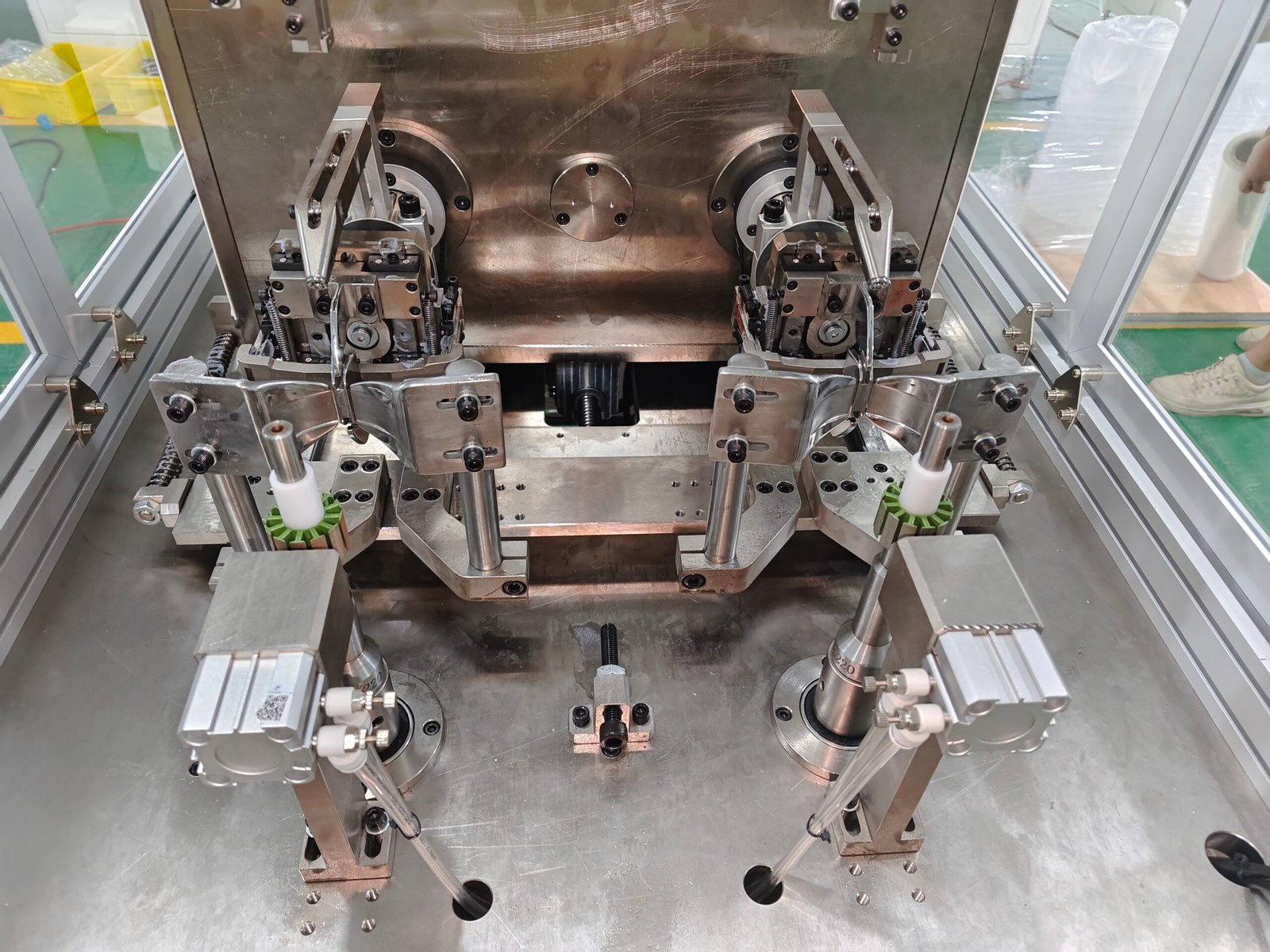
The winding methods of fully automatic stator winding machines are mainly divided into two types: external winding with a flying fork and internal winding with a pin. Wire arrangement methods include parallel arrangement, spiral arrangement, and cross arrangement. Specific characteristics are as follows:
1. External Winding with a Flying Fork
Applicable Scenarios: Stator with slots facing outwards (such as some brushed motors and external rotor motors).
Working Principle: The high-speed rotation of the flying fork drives the wire nozzle, which pulls the enameled wire into the stator slot, achieving precise wire arrangement.
Advantages: Economical and efficient, suitable for mass production; flying fork speed can reach 2600-5000 r/min, high winding efficiency.
2. Needle-type Internal Winding
Applicable Scenarios: Stator with inward-facing slots (e.g., brushless motors, internal rotor motors).
Working Principle: A servo motor drives the needle bar to move up and down at high speed, the wire nozzle moves synchronously, and the die moves left and right, realizing the coil winding into the slot.
Advantages: High winding accuracy, adaptable to complex slot shapes; needle bar speed can reach 800-1200 r/min, suitable for high-precision requirements.
3. Winding Methods
Parallel Winding: Wires are arranged in parallel, resulting in uniform magnetic field distribution and reduced vibration and noise; requires high-precision guide rails and tension control.
Helical Winding: Wires are spirally wound, resulting in high space utilization and a tight coil; requires high-speed winding capability and a compact structural design.
Cross-winding: Wires are arranged in a cross pattern, resulting in better magnetic field uniformity; requires complex winding control algorithms and tension compensation devices.
II. Core Measures to Ensure Parameter Accuracy
Parameter accuracy directly affects winding quality (such as number of turns, slot fill factor, and tension uniformity), requiring comprehensive assurance from three aspects: equipment configuration, control algorithm, and debugging and maintenance.
1. High-Accuracy Hardware Configuration
Winding Mechanism: Utilizes a servo motor to drive the winding head, coupled with precision guide rails and ball screws, achieving a positioning error ≤ ±0.05mm.
Tension Control System: Equipped with a brand-name servo tensioner, monitoring and dynamically adjusting tension in real time, with a fluctuation range ≤ ±0.5N, preventing wire breakage or coil loosening.
Die and Fixture: High-accuracy dies prevent wire scratching; the fixture positioning device and wire guiding device work closely together to ensure accurate wire guidance.
2. Intelligent Control Algorithm
PLC Servo Drive Controller: As the “brain” of the equipment, it ensures that the winding steps are executed according to the predetermined program through closed-loop control, with high data accuracy.
Motion Control Algorithm: Optimizes the winding path and speed, reducing inertial errors.
Visual Inspection System: Real-time scanning of the winding surface automatically corrects defects such as missing wires and overlaps, ensuring the copper wire fill rate meets design requirements.
3. Refined Debugging and Maintenance
Parameter Settings: Adjust winding speed, tension, number of turns, and other parameters according to stator size and wire specifications (e.g., wire diameter, slot distance). For example, thin wires require reduced tension to prevent breakage, while thicker wires require increased tension to ensure tightness.
Debugging Process:
Manual Mode Debugging: Adjust the relative positions of the needle bar, wire nozzle, and stator slot to ensure alignment accuracy.
Low-Speed Start: Observe whether the wire smoothly enters the slot without skipping or jamming.
Gradual Speed Increase: Monitor tension fluctuations and adjust the tensioner PID parameters to ensure tight and continuous wire winding.
Wire Laying Accuracy Verification: Use a laser rangefinder to check the wire spacing; error ≤ ±0.02mm.
Regular Maintenance: Clean the equipment surface and internal parts; inspect and replace worn parts (e.g., tensioner, wire nozzle, felt); regularly calibrate the controller and sensors to ensure data accuracy. 4. Environment and Operating Procedures
Environmental Control: Maintain workshop temperature between 20-30℃ and relative humidity ≤65% to prevent overheating of electronic components or short circuits in circuit boards.
Operating Procedures: Establish standardized operating procedures (SOPs), require operators to wear protective gear, and strictly prohibit reaching into the work area while the machine is running; regularly conduct fault simulation drills to improve emergency response capabilities.
What are the winding and wire arrangement methods of a fully automatic stator winding machine? How to ensure parameter accuracy? Vacuz has provided a simple explanation above, and we hope this information is helpful!
