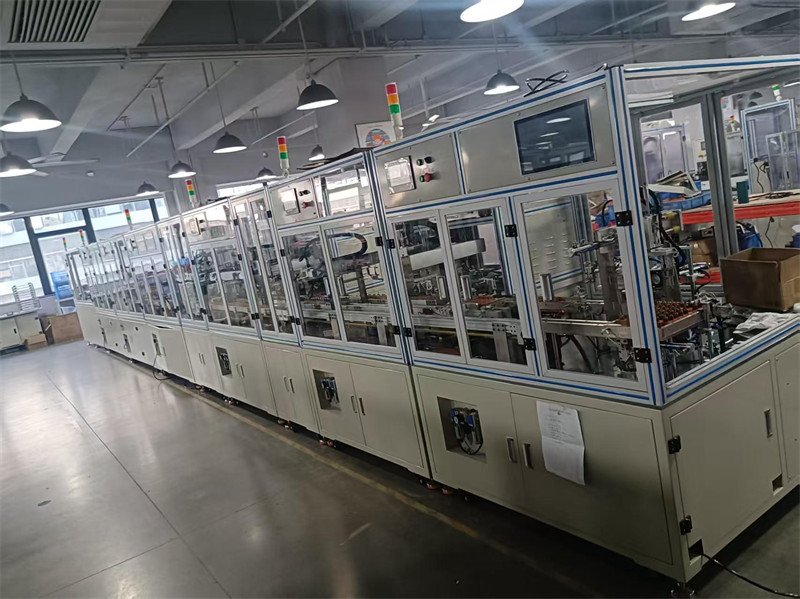
Motor rotor assembly can be performed in semi-automated or fully automated modes. Fully automated operations include loading and unloading rotor components. So, how is the precision of the rotor automatic loading and unloading production line controlled? What are the rotor requirements? Vacuz will explain.
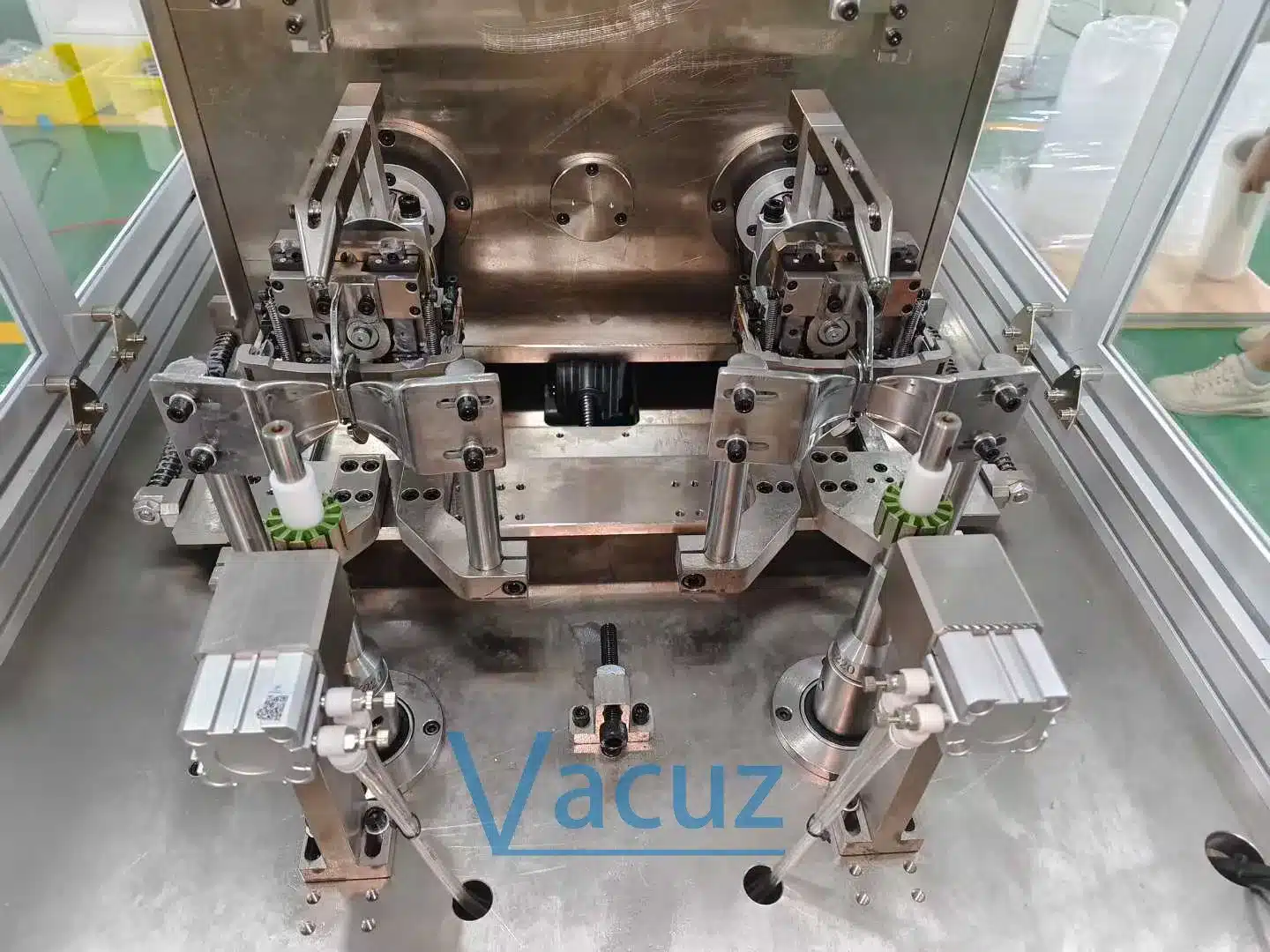
I. Production Line Precision Control Methods
1. High-Precision Equipment Configuration
Core Components: Servo motors, precision ball screws, and linear guides ensure accurate positioning.
Automated Equipment: High-precision press-fit equipment (pressure control ±0.1N), winding machines (tension fluctuation ≤ ±0.2N), and laser welders reduce human error.
Sensor System: Pressure/displacement/tension sensors provide real-time monitoring, and closed-loop control automatically adjusts (e.g., temperature monitoring to prevent insulation damage).
2. Modular and Flexible Design
Modular Structure: Independent functional modules (loading, positioning, assembly, and inspection) ensure that product changes require only the replacement of the fixture module.
Flexible Production: PLC + industrial robots enable rapid changeover between multiple product lines, reducing downtime by over 50%.
3. Online Inspection and Feedback Control
Key Process Inspection: AI visual recognition of 0.1mm defects (in processes such as magnet bonding and winding).
Feedback Adjustment: Sensor data triggers automatic correction of process parameters (e.g., speed reduction and voltage adjustment when tension exceeds the limit).
4. Standardization and Error-Proofing Design
SOP Specifications: Define standard procedures for magnet N/S pole assembly and dynamic balancing calibration.
Error-Proofing Devices: Sensors automatically shut down the machine if polarity errors are detected, and mechanical limiters prevent incorrect assembly.
5. Environmental and Material Control
Clean Environment: ISO Class 7 dust-free room with air filtration to prevent contamination.
Material Management: Full inspection of magnet coercivity (≥900kA/m) and silicon steel sheet thickness (≤0.35mm), using a WMS system to prevent mix-ups.
II. Specific Requirements for Rotors
1. Dimensional and Shape Accuracy
Core: Outer/Inner Diameter Tolerance ±0.05mm, Surface Free of Oil and Burrs.
Shaft Core: Roundness ≤0.01mm, Coaxiality ≥900kA/m, Avoid High-Speed Vibration.
2. Material Properties
Magnetic Steel: Remanence Br ≥1.2T, Coercivity HcJ ≥900kA/m, Low Hysteresis Loss.
Core: Silicon Steel Lamination Factor ≥0.95, Optimized Eddy Current Losses.
3. Assembly Process
Magnetic Steel Fixing: Adhesive + Press-Fit Combined Process, Pull-Off Force ≥50N.
Dynamic Balancing: Grade G2.5 (ISO 1940-1), Vibration Value ≤2.5mm/s.
4. Identification and Traceability
Polarity Marking: Laser marking or color-coded to distinguish between North and South poles.
Unique Code: Records production batches and test data, supporting full lifecycle traceability.
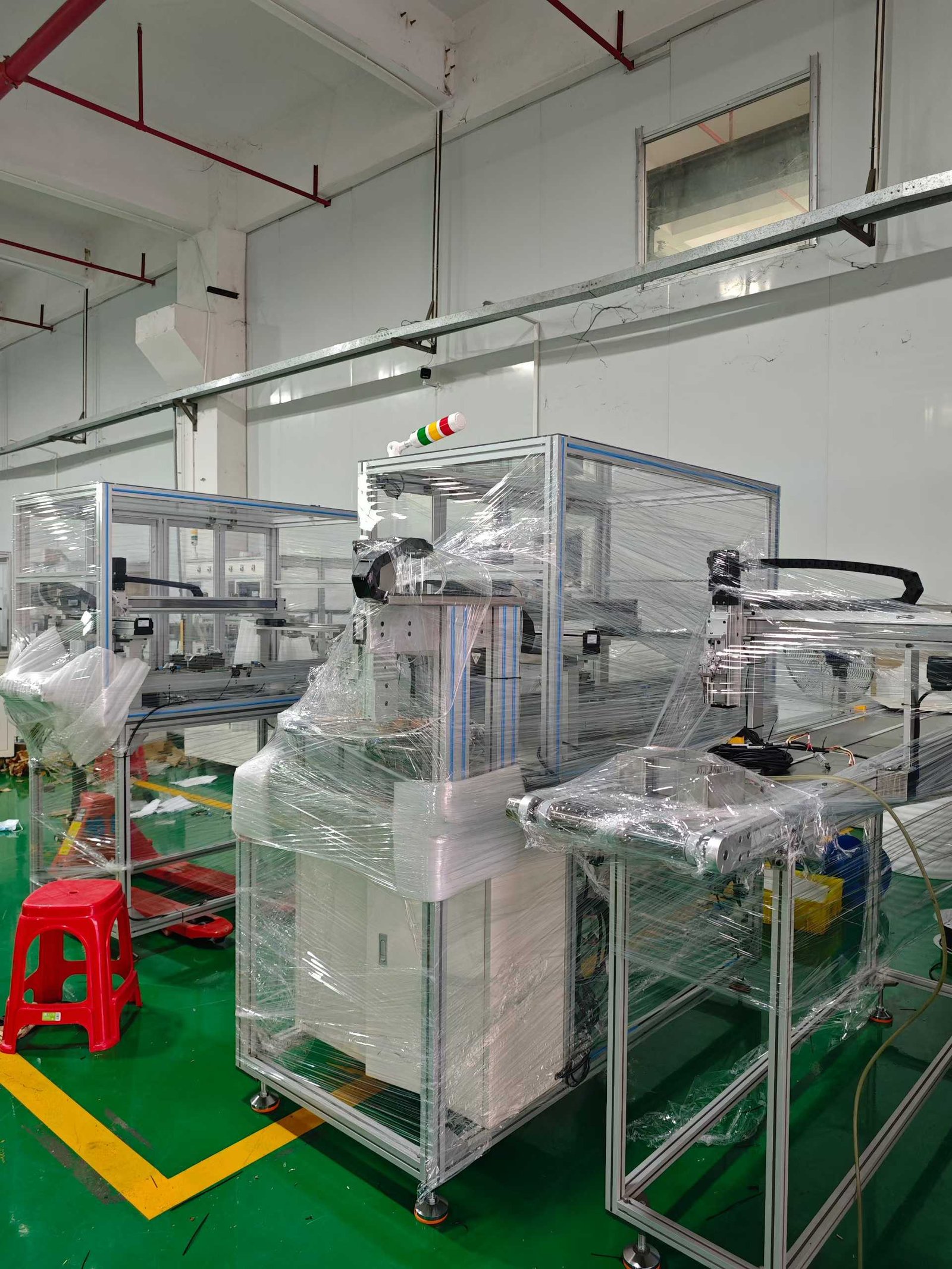

How do you control the accuracy of an automatic rotor loading and unloading production line? What are the rotor requirements? Vacuz has provided a brief explanation, and we hope this information is helpful!
电子邮件: sales@vacuz.com [fusion_form form_post_id=”431″ margin_top=”” margin_right=”” margin_bottom=”” margin_left=”” hide_on_mobile=”small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility” class=”” id=””][/fusion_form].

